query bookDetails {
bookById(id: "book-1") {
id
name
pageCount
author {
firstName
lastName
}
}
}Building a GraphQL service
Spring for GraphQL provides support for Spring applications built on GraphQL Java.
This guide walks you through the process of creating a GraphQL service in Java using Spring for GraphQL.
What You Will Build
You will build a service that will accept GraphQL requests at http://localhost:8080/graphql.
What You Need
-
About 15 minutes
-
A favorite text editor or IDE
-
Java 17 or later
-
You can also import the code straight into your IDE:
How to complete this guide
Like most Spring Getting Started guides, you can start from scratch and complete each step or you can bypass basic setup steps that are already familiar to you. Either way, you end up with working code.
To start from scratch, move on to Starting with Spring Initializr.
To skip the basics, do the following:
-
Download and unzip the source repository for this guide, or clone it using Git:
git clone https://github.com/spring-guides/gs-graphql-server.git -
cd into
gs-graphql-server/initial -
Jump ahead to A very short introduction to GraphQL.
When you finish, you can check your results against the code in gs-graphql-server/complete.
Starting with Spring Initializr
If you like, you can use this pre-populated Spring Initializr link to load the correct settings. Otherwise, continue on to manually set up the Initializr.
To manually initialize the project:
-
Navigate to https://start.spring.io. This service pulls in all the dependencies you need for an application and does most of the setup for you.
-
Choose either Gradle or Maven and the language you want to use. This guide assumes that you chose Java.
-
Click Dependencies and select Spring for GraphQL and Spring Web.
-
Click Generate.
-
Download the resulting ZIP file, which is an archive of a GraphQL application that is configured with your choices.
| If your IDE has the Spring Initializr integration, you can complete this process from your IDE. |
| You can also fork the project from GitHub and open it in your IDE or other editor. |
A very short introduction to GraphQL
GraphQL is a query language to retrieve data from a server. It is an alternative to REST, SOAP, or gRPC. In this tutorial, we will query the details for a specific book from an online store backend.
This is an example request you can send to a GraphQL server to retrieve book details:
This GraphQL request says:
-
perform a query for a book with id "book-1"
-
for the book, return id, name, pageCount and author
-
for the author, return firstName and lastName
The response is in JSON. For example:
{
"bookById": {
"id":"book-1",
"name":"Effective Java",
"pageCount":416,
"author": {
"firstName":"Joshua",
"lastName":"Bloch"
}
}
}An important feature of GraphQL is that it defines a schema language, and that it is statically typed. The server knows exactly what types of objects requests can query and what fields those objects contain. Furthermore, clients can introspect the server to ask for schema details.
| The word schema in this tutorial refers to a "GraphQL Schema", which is not related to other schemas like "JSON Schema" or "Database Schema". |
The schema for the above query is:
type Query {
bookById(id: ID): Book
}
type Book {
id: ID
name: String
pageCount: Int
author: Author
}
type Author {
id: ID
firstName: String
lastName: String
}This tutorial will focus on how to implement a GraphQL server with this schema in Java.
We’ve barely scratched the surface of what’s possible with GraphQL. Further information can be found on the official GraphQL page.
Our example API: getting book details
These are the main steps to create a server with Spring for GraphQL:
-
Define a GraphQL schema
-
Implement the logic to fetch the actual data for a query
Our example app will be a simple API to get details for a specific book. It is not intended to be a comprehensive API.
Schema
In your Spring for GraphQL application prepared earlier, add a new file schema.graphqls to the src/main/resources/graphql folder with the following content:
type Query {
bookById(id: ID): Book
}
type Book {
id: ID
name: String
pageCount: Int
author: Author
}
type Author {
id: ID
firstName: String
lastName: String
}Every GraphQL schema has a top-level Query type, and the fields under it are the query operations exposed by the application. Here the schema defines one query called bookById that returns the details of a specific book.
It also defines the types Book with fields id, name, pageCount and author, and the type Author with fields firstName and lastName.
| The Domain Specific Language used above to describe a schema is called the Schema Definition Language or SDL. For more details, see the GraphQL documentation. |
Source of the data
A key strength of GraphQL is that data can be sourced from anywhere. Data can come from a database, an external service, or a static in-memory list.
To simplify the tutorial, book and author data will come from static lists inside their respective classes.
Create the Book and Author data sources
Let’s now create the Book and Author classes in the main application package, right next to GraphQlServerApplication. Use the following as their content:
package com.example.graphqlserver;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public record Book (String id, String name, int pageCount, String authorId) {
private static List<Book> books = Arrays.asList(
new Book("book-1", "Effective Java", 416, "author-1"),
new Book("book-2", "Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy", 208, "author-2"),
new Book("book-3", "Down Under", 436, "author-3")
);
public static Book getById(String id) {
return books.stream()
.filter(book -> book.id().equals(id))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
}
}package com.example.graphqlserver;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public record Author (String id, String firstName, String lastName) {
private static List<Author> authors = Arrays.asList(
new Author("author-1", "Joshua", "Bloch"),
new Author("author-2", "Douglas", "Adams"),
new Author("author-3", "Bill", "Bryson")
);
public static Author getById(String id) {
return authors.stream()
.filter(author -> author.id().equals(id))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
}
}Adding code to fetch data
Spring for GraphQL provides an annotation-based programming model. With controller annotated methods, we can declare how to fetch the data for specific GraphQL fields.
Add the following to BookController.java in the main application package, next to Book and Author:
package com.example.graphqlserver;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.Argument;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.QueryMapping;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.SchemaMapping;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class BookController {
@QueryMapping
public Book bookById(@Argument String id) {
return Book.getById(id);
}
@SchemaMapping
public Author author(Book book) {
return Author.getById(book.authorId());
}
}By defining a method named bookById annotated with @QueryMapping, this controller declares how to fetch a Book as defined under the Query type. The query field is determined from the method name, but can also be declared on the annotation itself.
Spring for GraphQL uses RuntimeWiring.Builder that registers each such controller method as a GraphQL Java graphql.schema.DataFetcher. A DataFetcher provides the logic to fetch the data for a query or for any schema field. The Spring Boot starter for GraphQL has auto-configurations that automates this registration. |
In the GraphQL Java engine, DataFetchingEnvironment provides access to a map of field-specific argument values. Use the @Argument annotation to have an argument bound to a target object and injected into the controller method. By default, the method parameter name is used to look up the argument, but can also be specified on the annotation itself.
This bookById method defines how to get a specific Book, but does not take care of fetching the related Author. If the request asks for the author information, GraphQL Java will need to fetch this field.
The @SchemaMapping annotation maps a handler method to a field in the GraphQL schema and declares it to be the DataFetcher for that field. The field name defaults to the method name, and the type name defaults to the simple class name of the source/parent object injected into the method. In this example, the field defaults to author and the type defaults to Book.
For more, see the documentation for the Spring for GraphQL annotated controller feature.
That’s all the code we need!
Let’s run our first query.
Running our first query
Enable the GraphiQL Playground
GraphiQL is a useful visual interface for writing and executing queries, and much more. Enable GraphiQL by adding this config to the application.properties file.
spring.graphql.graphiql.enabled=trueBoot the application
Start your Spring application. Navigate to http://localhost:8080/graphiql.
Run the query
Type in the query and click the play button at the top of the window.
query bookDetails {
bookById(id: "book-1") {
id
name
pageCount
author {
id
firstName
lastName
}
}
}You should see a response like this.
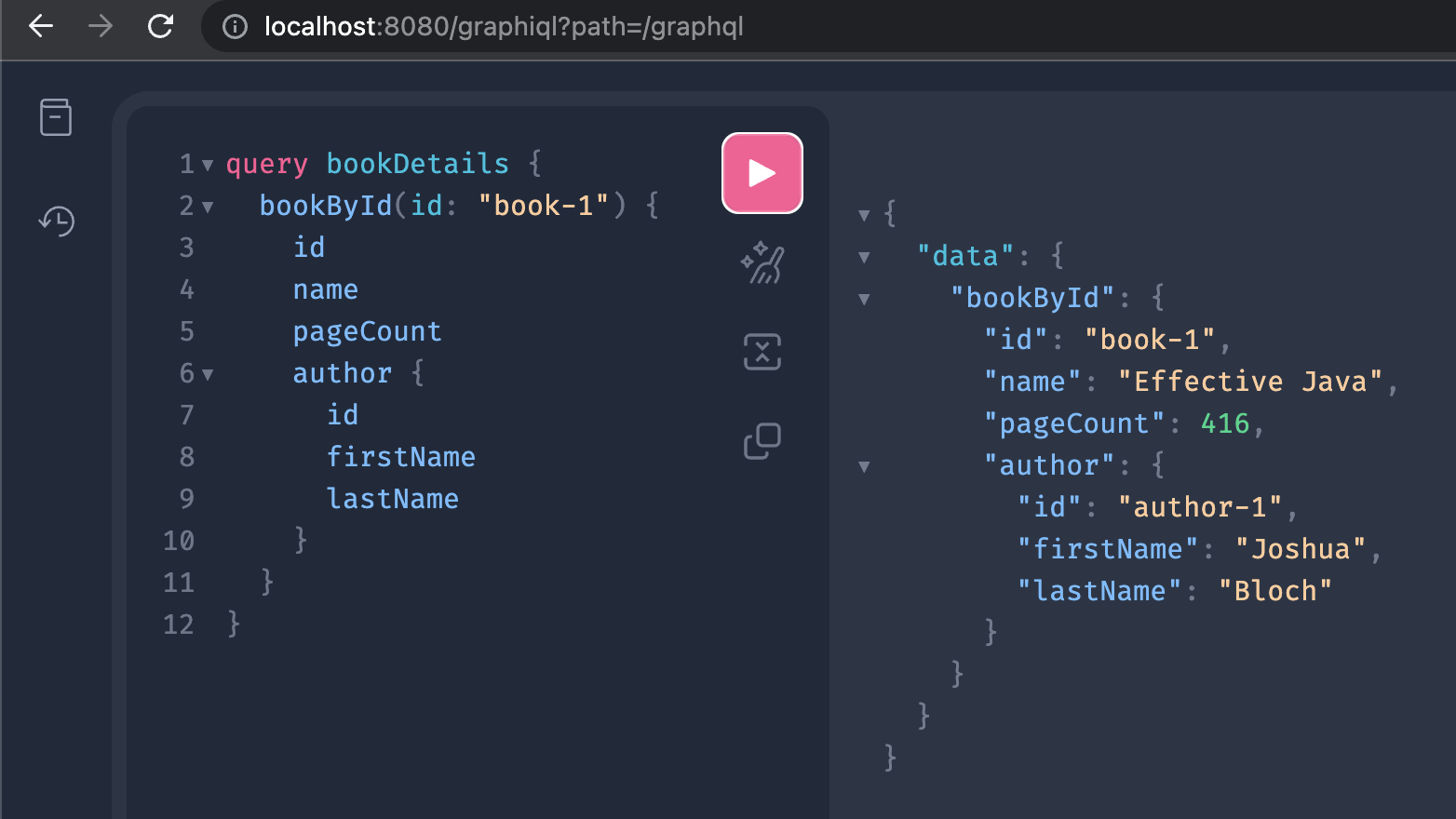
Congratulations, you have built a GraphQL service and executed your first query! With the help of Spring for GraphQL, you were able to achieve this with only a few lines of code.
Testing
Spring for GraphQL provides helpers for GraphQL testing in the spring-graphql-test artifact. We have already included this artifact as part of the project generated by Spring Initializr.
Thoroughly testing a GraphQL service requires tests with different scopes. In this tutorial, we will write a @GraphQlTest slice test, which focuses on a single controller. There are other helpers to assist with full end-to-end integration tests and focused server side tests. For the full details, see the Spring for GraphQL Testing documentation and Auto-configured Spring for GraphQL tests in the Spring Boot documentation.
Let’s write a controller slice test that verifies the same bookDetails query requested in the GraphiQL playground a few moments ago.
Add the following to a test file BookControllerTests.java. Save this file in a location within the src/test/java/com/example/graphqlserver/ folder.
package com.example.graphqlserver;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.graphql.test.autoconfigure.GraphQlTest;
import org.springframework.graphql.test.tester.GraphQlTester;
@GraphQlTest(BookController.class)
public class BookControllerTests {
@Autowired
private GraphQlTester graphQlTester;
@Test
void shouldGetFirstBook() {
this.graphQlTester
.documentName("bookDetails")
.variable("id", "book-1")
.execute()
.path("bookById")
.matchesJson("""
{
"id": "book-1",
"name": "Effective Java",
"pageCount": 416,
"author": {
"firstName": "Joshua",
"lastName": "Bloch"
}
}
""");
}
}This test refers to a GraphQL query similar to what we used in the GraphiQL Playground. It’s parameterized with an $id to make it reusable. Add this query in a bookDetails.graphql file located in src/test/resources/graphql-test.
query bookDetails($id: ID) {
bookById(id: $id) {
id
name
pageCount
author {
id
firstName
lastName
}
}
}Run the test and verify that the result is identical to the GraphQL query manually requested in the GraphiQL Playground.
The @GraphQlTest annotation is useful for writing controller slice tests, which are focused on a single controller. @GraphQlTest auto-configures the Spring for GraphQL infrastructure, without any transport nor server being involved. Automatic configuration enables us to write tests faster by skipping boilerplate code. As this is a focused slice test, only a limited number of beans are scanned including @Controller and RuntimeWiringConfigurer. For the list of scanned beans, see the documentation.
GraphQlTester is a contract that declares a common workflow for testing GraphQL requests, independent of transport. In our test, we provide a document with documentName with the required variables, then execute the request. We then select a part of the response with its JSON path and assert that the JSON at this location matches the expected result.
Congratulations! In this tutorial you built a GraphQL service, ran your first query, and wrote your first GraphQL test!
Further reading
Sample source code
This guide has been written in collaboration with the GraphQL Java team. Huge thanks to Donna Zhou, Brad Baker, and Andreas Marek! The source code for this tutorial can be found on GitHub.
Documentation
Read the Spring for GraphQL documentation.
GraphQL Java is the GraphQL engine powering Spring for GraphQL. Read the GraphQL Java documentation.
More Spring for GraphQL examples
See more samples in the dedicated repository.
Stack Overflow questions
You can raise questions on Stack Overflow with the spring-graphql tag.
Want to write a new guide or contribute to an existing one? Check out our contribution guidelines.
| All guides are released with an ASLv2 license for the code, and an Attribution, NoDerivatives creative commons license for the writing. |