Get ahead
VMware offers training and certification to turbo-charge your progress.
Learn moreGetting started with Spring Cloud can be daunting. If you have seen the great Josh Long give his Cloud Native Java presentation, you will notice that you need to create several supporting applications before you can see your application at work.
As part of the transition from Spring XD to Spring Cloud Dataflow, one of the extracted projects is called the Spring Cloud Deployer. The Deployer allows for launching applications on various platforms, including launching on a developer machine.
We wanted to simplify users' ability to experiment with Spring Cloud, so the spring cloud command was born.
The spring cloud command automatically runs some of the supporting servers required to run applications in a Spring Cloud environment such as Config Server and Eureka.
The first step is to install the Spring Boot CLI (the spring command). The required minimum version is 1.4.1.RELEASE. I prefer the SDKMAN method myself.
$ sdk install springboot
$ spring --version
Spring Boot v1.4.1.RELEASE
Next you need to install the Spring Cloud Launcher CLI (the spring cloud command) via the Spring Boot CLI.
$ spring install org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-cli:1.2.1.RELEASE
If you run spring cloud without any arguments, Config Server and Eureka are launched. Config Server starts before other services so that it will available so those other services can pull their configuration.
The following servers are available to launch:
$ spring cloud --list
configserver dataflow eureka h2 hystrixdashboard kafka zipkin
To run a specific set of servers, simply list them as arguments:
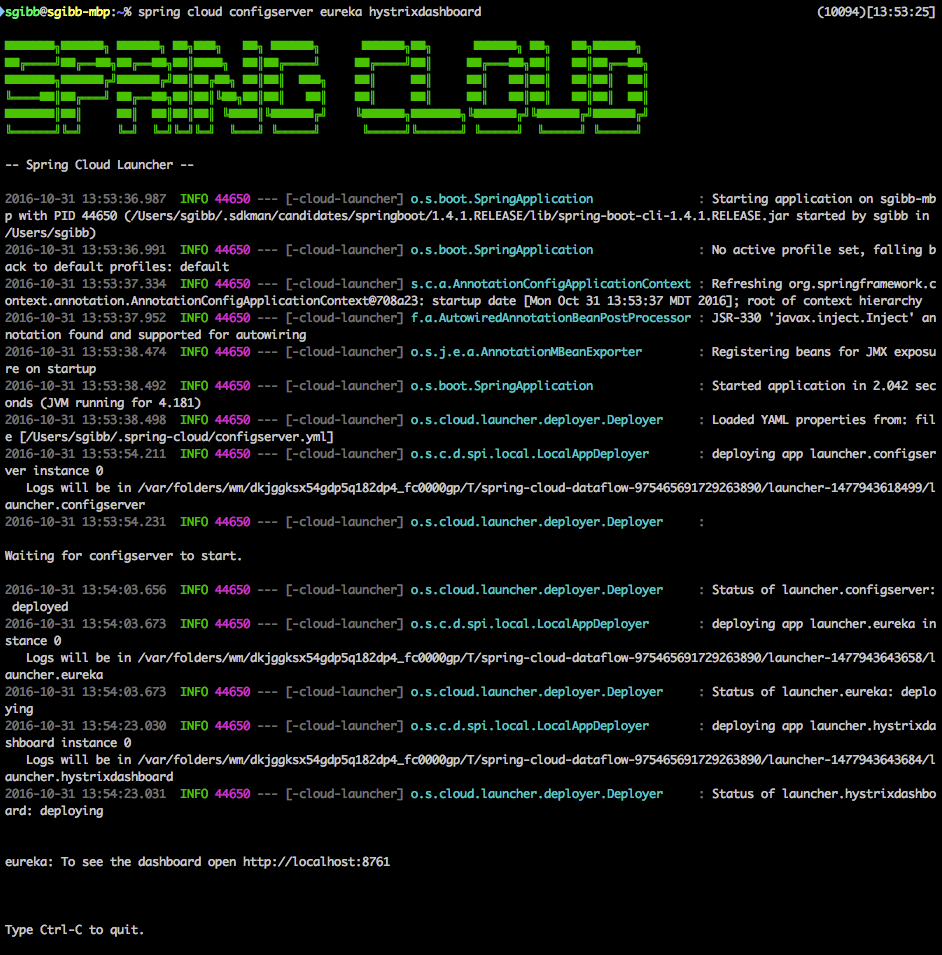
$ spring cloud configserver eureka hystrixdashboard
The previous command runs Config Server, Eureka and the Hystrix Dashboard.
$ spring help cloud
spring cloud - Start Spring Cloud services, like Eureka, Config Server, etc.
Option Description
------ -----------
-d, --debug Debug logging for the deployer
-l, --list List the deployables (don't launch
anything)
-v, --version Show the version (don't launch
examples:
Launch Eureka:
$ spring cloud eureka
Launch Config Server and Eureka:
$ spring cloud configserver eureka
List deployable apps:
$ spring cloud --list
Show version:
$ spring cloud --version
Each process can be configured using normal Spring Boot external configuration files with a special name and location. The name of the file is based off of the name of the process (again see spring cloud --list for the full list). Config Server, for example could be configured in a file named configserver.yml or configserver.properties. The search path for the configuration files is the current directory (.), ./config and $HOME/.spring-cloud/.
By default, the configserver process uses the native profile and configuration in its JAR. As an example, let's configure Config Server globally to load properties from a GitHub repository. The contents of $HOME/.spring-cloud/configserver.yml could be:
spring:
profiles:
active: git
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/spring-cloud-samples/config-repo
| Process | Port | URL |
|---|---|---|
configserver |
8888 | /info |
eureka |
8761 | N/A |
hystrixdashboard |
7979 | /hystrix |
dataflow |
9393 | /dashboard |
kafka |
9092 | N/A |
zipkin |
9411 | N/A |
h2 |
9095 | / |
The URL column is what gets registered with Eureka (if running). This allows you to click on the instance links in the Eureka dashboard.
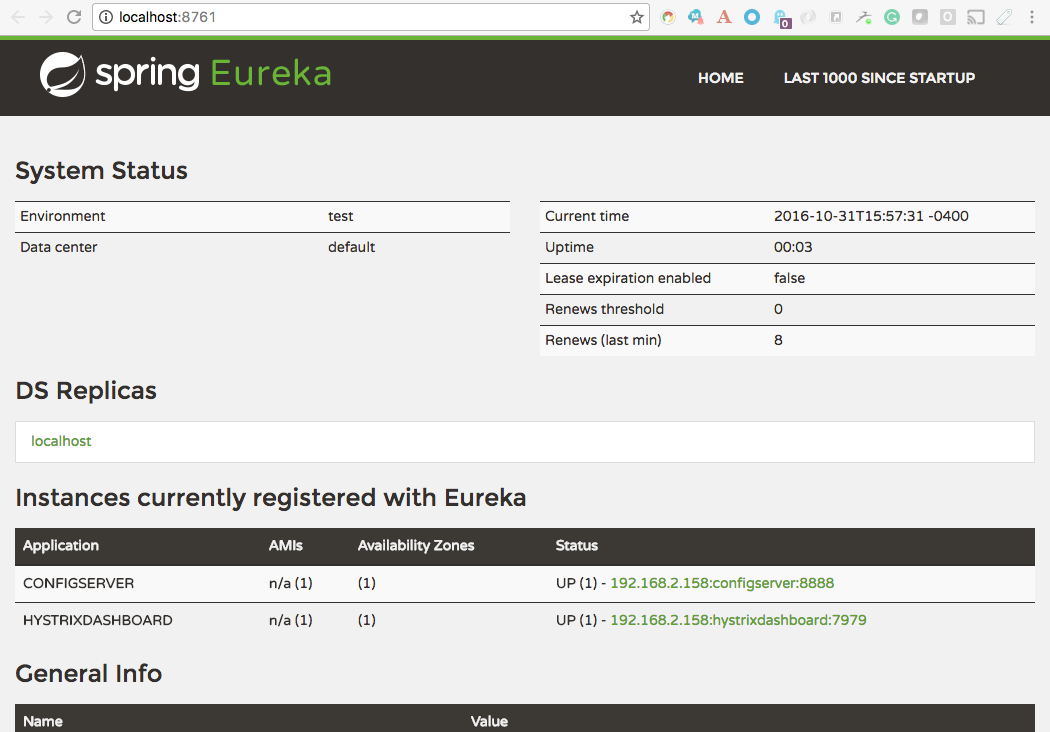
If a process registers with Eureka, it will use the value in the Process column as spring.application.name.
The kafka process also starts ZooKeeper on port 2181. Kafka is used for the Spring Cloud Bus.
The h2 database is available on port 9096 with the following JDBC URL: jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost:9096/./target/test. The H2 URL can be customized via the spring.datasource.url property.
Please check out the project on GitHub. The team would appreciate issues and enhancement requests from the community.