The Spring Web Flow project team has just completed the 7th maintenance release of Web Flow 2. This is our best release to-date and comes nearly one year to the day of the Web Flow 2.0.0 final release. Now, with the 2.0.x line mature and stable, we are beginning work on the next major version. In this entry, I would like to reflect on the past year and also provide some information on where we are headed.
Web Flow 2 Adoption
When Web Flow 2 was released last year, we saw 50,000 downloads in the first two months after the release. Since then, our forum traffic has steadily increased, and we have seen new adoption across several exciting industries. Many of you know Spring Web Flow is the foundation of Orbitz's on-line travel platform which today powers sites such as ebookers.com and nwa.com. If you have been following the 2009 NBA playoffs, you may also find it interesting Web Flow is an important component of nba.com as well.
Our Work in the Past Year
Like all Spring projects, Web Flow depends on feedback to be successful. Field interactions with customers and SpringSource support engineers have driven much of our work on 2.0.x in the last year. The community has also been exceptional at reporting bugs, contributing patches, highlighting usage scenarios, and generally discussing ways the project can continue to improve.
I'd like to quickly recap some of the concrete improvements made since 2.0.0.RELEASE:
-
Configuration simplifications and conventions for flow URL mapping
This one, applied in 2.0.5 and driven by customer feedback as well as Dan Allen's JSFOne presentation, cut the size of a typical webflow-config.xml in half, down to ~20 lines of configuration. As you can see, this was achieved by applying a wildcard-search for flow definitions in conjunction with conventions for binding flow definitions to URLs based on their flow ids.
-
Support for explicit view-state model bindings
This improvement, first provided to SpringSource customers in response to this security advisory and subsequently released in 2.0.3, allows you to restrict the set of allowed model bindings by view-state. This was achieved in the declarative style shown here.
Redirect-after-post improvements
One of the most useful features of Web Flow is the redirect-after-post pattern just works, which is one critical prerequisite to good back button support with controlled navigation. 2.0.5, 2.0.6 and 2.0.7 all introduced subsequent improvements to this support. The most recent improvement ensures redirect behavior is applied consistently in all scenarios, including when there is a binding or validation error. You can review the source code that controls the enforcement of this pattern in the doEnter and doResume methods of ViewState.java.
Support for streaming actions
The community figured out how to stream files back to a client participating in a flow. Documented support for this was overlooked in Web Flow 2.0.0 and was added in 2.0.6.
Type conversion improvements
Numerous improvements to the system that powers view-state model binding were applied from 2.0.2 through 2.0.6. The system provides all the unique features of Spring's DataBinder, such as support for converting elements of generic collections, with a simpler type Converter API compared to Java PropertyEditors.
In addition to these core improvements, we have seen a number interesting Web Flow integrations in the last year such as Grails 1.1, the ZK RIA framework, Terracotta, IceFaces, SpringSource's richweb training course, IntelliJ, Skyway Software, and the first Web Flow 2 book.
Where We Are Headed
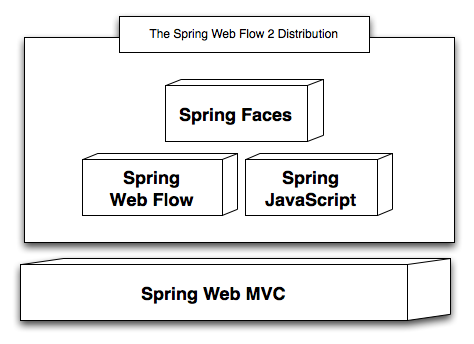
We have a lot planned for the future. I will leave all the technical details for another time, but would like to summarize some of the key themes of the effort. First, Web Flow 3 will be the first release to require Java 5, as it will build on Spring Framework 3 as its foundation. Second, you can expect to see the introduction of a @Flow model that compliments Spring MVC's stateless @Controller model and allows stateful web flows to be defined as POJOs. Third, you can expect Spring JavaScript and Spring Faces, two modules that grew out of the Web Flow 2 effort, to both be promoted to top-level Spring projects. Spring JavaScript will become Spring's official Ajax integration project, and Spring Faces will become Spring's official JavaServerFaces integration project.
I look forward to meeting with many of you at SpringOne next week to discuss your experiences applying the project and our future directions!